| Wound care | Orthotics | laser treatment |
 |
 |
 |
| Foot/Ankle Pain and Injury | Toe Deformity | Foot Deformity |
 |
 |
 |
| Lymphedema | Fungus | Healthy Feet |
 |
 |
 |
Wound Care
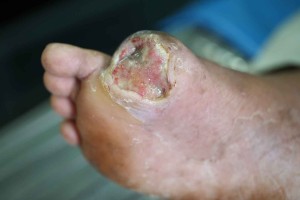
What are foot and toe ulcers?
An ulcer is an open wound or sore that will not heal or keeps returning. When you have ulcers on your feet and toes, it can be related to diabetes specifically, a complication called neuropathy that causes you to lose feeling in your feet. A scrape, cut or puncture in your skin can turn into an ulcer, but you might not know it’s there if you have neuropathy.
Ulcers can lead to infections. Sometimes, the infection won’t go away and you may need to have part of your foot or toe surgically removed (amputated). About 15% of people with diabetes will get a foot or toe ulcer. Around 14% to 24% of people with diabetes in the U.S. need an amputation after they get an ulcer.
Who gets foot and toe ulcers?
Foot and toe ulcers can happen to many people but might be more common in Black, Native American and Hispanic people. If you have an eye, kidney or heart disease related to diabetes, you’re also at a higher risk. About 15% of people with diabetes will get an ulcer, typically on the bottom of their foot. Some of those people will be hospitalized because of complications.
You’re also at a higher risk of getting foot and toe ulcers if you have any of the following conditions:
- Blood circulation issues.
- Heart Disease.
- Obesity.
- A foot condition like a bunion or hammertoe.
- Kidney Disease.
- Lifestyle behaviors like using tobacco and alcohol can also increase your risk of developing ulcers on your feet or toes.
What do foot and toe ulcers look like?
Ulcers are open wounds in your skin that can take on almost any shape. Some shapes are more common than others on specific parts of your body. For example, ulcers on your foot or toe might be shaped like a crater or a wedge.
Foot and toe ulcers vary in color. The most common colors are:
- Black.
- Grey.
- Red.
- Pink.
- Yellow.
If your ulcer is black, that means cells in the tissues have died. This is called necrosis (gangrene).
How big are foot and toe ulcers?
There are many different sizes of ulcers. They start as small as 1 centimeter wide (about the size of a pea or a Cheerio) and can grow to the size of your entire foot if left untreated.
The depth of the ulcer can change, too. Several different classification systems exist to define the depth of an ulcer. The Wagner Diabetic Foot Ulcer Grade Classification System, for example, has six grades:
- Grade 0: Your skin is intact (undamaged).
- Grade 1: The ulcer is “superficial,” which means that the skin is broken but the wound is shallow (in the upper layers of the skin).
- Grade 2: The ulcer is a “deep” wound.
- Grade 3: Part of the bone in your foot is visible.
- Grade 4: The forefront of your foot (the section closest to your toes) has gangrene (necrosis).
- Grade 5: The entire foot has gangrene.
How can I tell if I’m getting an ulcer on my foot or toe?
When an ulcer is starting to develop on your foot or toe, you might notice changes in your skin like:
- Cracked skin.
- Dry skin.
- Scaly skin.
- Redness.
- Rashes.
As the ulcer gets worse, it can get wider, and longer and deeper — sometimes down to the bone. In advanced stages you might see:
- A callus.
- A halo (ring) around the center of the wound that feels harder than the skin around it.
- Drainage (you might see this in your socks when you take them off), which is a sign that you might have an infection.
- A brown discoloration.
- A strong odor.
How are foot and toe ulcers diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can tell what type of ulcer you have based on four observations:
- The appearance of the ulcer.
- Location of the ulcer.
- The appearance of the borders.
- The appearance of the surrounding skin.
Your primary healthcare provider can diagnose an ulcer, but they might send you to a specialist for treatment. You might see a podiatrist, a provider who works with feet, or a wound specialist. For more complicated cases that require surgery, you might also see a plastic surgeon, anesthesiologist, orthopedic surgeon and/or vascular surgeon.
What tests are done to determine if I have a foot or toe ulcer?
To find out precisely how deep the ulcer goes, and to see if it caused an infection in a nearby bone, they might order a:
- X-Ray.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
What are the types of foot and toe ulcers?
Two types of ulcers can affect your feet and toes:
- Neurotrophic (diabetes-related) ulcers.
- Arterial (ischemic) ulcers.
What are neurotrophic ulcers?
Neurotrophic ulcers occur primarily in people with diabetes, although they can affect anyone who has impaired sensation in their feet. They can be found anywhere on your feet, but they usually develop on the parts of your feet and toes that are most sensitive to weight (pressure points).
Neurotrophic ulcers don’t cause pain. But they can be serious if they aren’t treated promptly or they don’t respond to treatment.
A neurotrophic ulcer might be the following colors:
- Black.
- Brown.
- Red.
- Pink.
- Any combination of those colors.
The thin borders of the ulcers are “punched out,” meaning that they’re taller than the surrounding tissues.
What are arterial ulcers?
A condition called peripheral arterial disease can reduce blood flow to your extremities. When this happens, your foot tissue may start to die. The ulcers that form from reduced blood flow are called arterial ulcers.
The word “arterial” means “relating to arteries.” Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from your heart to the rest of your body, including your feet and toes. Anyone can get an arterial ulcer, but people who smoke or have diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol are at higher risk.
Unlike neurotrophic ulcers, arterial ulcers can form on many parts of your body, including:
- On your heels.
- On the tips of your toes.
- Between your toes (where your toes rub together).
- The bony parts of your feet and toes that rub against bed sheets, socks or shoes.
- The nail bed (if your toenail cuts into your skin, if your toenail was trimmed aggressively or if you had an ingrown toenail removed).
Arterial ulcers are:
- Black.
- Brown.
- Grey.
- Yellow.
Arterial ulcers don’t bleed. The borders and surrounding skin usually appear taller. If you have an infection or experience irritation, you might see swelling and redness around the base of the ulcer. The redness often turns to a pale white or yellow color if you elevate your leg. Arterial ulcers are typically very painful, especially at night.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
There are many possible reasons why you might get foot and toe ulcers. Here are some of the most common:
- Neuropathy from diabetes.
- Cellulitis, a common bacterial infection.
- Trauma to the foot or toe.
- Poor circulation (caused by a variety of conditions).
- Peripheral artery disease.
- Unusually formed toes.
- An unusual walk that puts too much pressure on one part of your foot or toe.
- Friction when your foot or toe rubs against the toe box of your shoe.
Although they don’t cause ulcers, foot and toe ulcers are often found alongside toe conditions such as hammertoe, mallet toe and claw toe.
Are foot and toe ulcers contagious?
Contagious means that you can spread the condition from one person to another person. Root ulcers aren’t like other foot conditions and can not be passed from person to person. So if you are worried about spreading or catching a foot or toe ulcer, dont, you cant.
CARE AND TREATMENT
The treatment of all ulcers begins with careful skin and foot care. Inspecting your skin is very important, especially for people with diabetes. Detecting and treating foot and toe sores early can help you prevent infection and keep the sore from getting worse.
The goal of treating a foot or toe ulcer is to heal your wound and relieve pain. Your treatment plan will be individualized based on what medical condition is causing your ulcers. Correcting the cause of your ulcer is very important so it won’t come back after treatment.
There are both surgical and nonsurgical treatments for foot and toe ulcers. For early-stage foot and toe ulcers, nonsurgical treatments might work. More advanced ulcers — especially ones that are infected — might require surgery.
Nonsurgical treatments include:
- Topical wound care. (Ulcers have less of a risk of infection and heal faster if they’re kept covered and moist.)
- Antibiotics.
- Antiplatelet or anticlotting medications.
- Compression clothes.
- Draining.
- Prosthetics.
- Orthotics.
- Removing pressure from the area by wearing a cast, a certain shoe or braces. You might need to use crutches or a wheelchair. This is called nonsurgical off-loading.
- Elevation of the foot.
Invasive and surgical treatments include:
- Debridement (the removal of infected tissue).
- Hammertoe Repair.
- Plantar exostectomy (the removal of parts of the sole of the foot).
- Achilles tendon lengthening (the stretching of the tendon).
- Metatarsal osteotomies (the metatarsal bone of the big toe is cut and realigned).
- Shaving or removing bones.
- Tenotomy (the removal of scar tissue).
- Reconstructive surgery using skin grafts.
How do I take care of my foot and toe ulcers?
Your healthcare provider might teach you how to care for your ulcers at home. You might be instructed to:
- Wash the affected area with mild soap.
- Keep the wound clean and dry.
- Change the bandages as directed.
- Take prescribed medications as directed.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Ask your healthcare provider how much water you should drink every day.
- Follow a healthy diet, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Exercise regularly, under your healthcare provider’s care.
- Wear appropriate shoes.
- Wear compression wraps as directed.
How long does it take for an ulcer to heal?
It might take weeks to months for an ulcer to heal (with treatment).
How can I reduce my risk of foot and toe ulcers?
There are several things you can do to help reduce your risk of getting foot and toe ulcers. Sometimes, adopting these habits can even stop them from coming back. Try to:
- Manage your diabetes. If you have diabetes you should wear appropriate footwear and never walk barefoot.
- Examine your legs as well as the tops and bottoms of your feet and the areas between your toes every day. Look for any blisters, cuts, cracks, scratches or other sores. Also check for redness, increased warmth, ingrown toenails, corns and calluses. Use a mirror to view your leg or foot if necessary. If it’s difficult to see, ask a family member to look at the area for you. See a healthcare provider immediately if you notice any problems.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about ways you can stop smoking.
- Manage your blood pressure.
- Regulate your cholesterol and triglyceride levels by changing your diet. Limit salt in your diet.
- Care for your toenails frequently. Cut your toenails after bathing, when they are soft. Cut toenails straight across and smooth with a nail file. Take care of ingrown toenails.
- Exercise.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- See your podiatrist often.
- Wear appropriate shoes and socks. Talk to your podiatrist about what you need.
WHEN TO CALL THE DOCTOR
If you have diabetes, it’s important to see a podiatrist regularly. Whether you have diabetes or not, you should see a healthcare provider immediately if you find an ulcer on your foot or toe. Left untreated, it could get infected, leading to complications like amputations.
A note from Aveon Health
It can be distressing to discover an open sore on your foot or toe, especially not knowing what may have what caused it The wound may not be might not be healing and if you have neuropathy from diabetes, you might not even feel it. Please know that your healthcare provider can successfully treat your ulcer, especially if it’s found early. If left untreated, an ulcer can lead to serious complications, like serious infections that may lead to you being hospitalized.
If you have neuropathy caused by diabetes, remember that it’s important to check your feet and toes on a regular basis. Check your toes and feet every time you shower or when you go to put on your shoes. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you find an ulcer.
Diabetes is a systemic disease affecting many organs of the body, ideal care requires a team tactic. We at Aveon Health can help by involving the podiatrist as well as the family physician to jointly care for your feet and your condition.
What are orthotics?
Your feet rely on balance to give you proper support, so any time there’s a problem that interrupts this delicate system, you may subjected to injury or pain. Orthotics are designed to restore balance to the structure of your feet and to provide support to relieve your discomfort and problems down the road.
Orthotics come in full-foot lengths or as inserts that address only one area of your foot, such as your heels or your arches.
Why would I need orthotics?
There are a number of reasons why you may need orthotics, which are designed in one of two ways:
Functional orthotics
If you have a structural irregularity, such as flatfoot or high arches, orthotics correct the condition, allowing you to walk more naturally and avoid discomfort and prevent injury. They also allow you more mobility by offsetting painful conditions, such as:
-
Bursitis
-
Tendinitis
-
Plantar fasciitis
-
Arthritis
Aside from issues that directly affect your feet, structural problems can also create issues in outlying areas, such as your knees, hips, and back. For example, if you don’t have enough support in your arches, your ankles may roll inward, greatly affecting the alignment of your knee and hip joints. As a result, these joints don’t function properly as they accommodate your abnormal stance and gait, which can lead to pain.
Accommodative orthotics
If you have painful conditions, like calluses on the bottom of your feet or stone bruises, orthotics provide extra cushioning to relieve the discomfort.
Why should I get custom orthotics?
There are many companies that offer various kinds of over-the-counter foot inserts. The products may provide some support but remember that these products are not specifically designed and molded to your feet. For best results consult with your provider and have custom orthotics made especially for you, your feet will thank you.
During your visit your doctor will evaluate your feet and determine the best treatment and if orthotics are needed they make molds of your feet. These molds will be sent off to a lab for custom manufacture of your orthotics. Custom orthotics, are made to address your unique issues. Custom orthotics are made from highly durable materials which means that they will last a long time and not have to be replaced every few of months like you have to do with over-the-counter products.
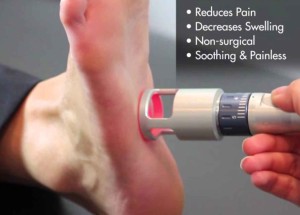
Laser Treatment:
What is Foot Laser Therapy?
Lasers are often associated with industrial applications like cutting through metal or drilling holes in stone, but they also have other less-industrial applications too.
In podiatry, lasers are a tried and tested type of treatment used to accelerate healing in a wide range of foot conditions.
Although foot lasers are not yet at the level seen in Si-Fi movies that result in instant healing, they do provide significant enough benefits when used.
If you have been wondering, “what is foot laser therapy?” we cover all the must-know points below.
How does foot laser therapy work?
Foot lasers therapy works by accelerating healing, especially in soft tissue and tendons. Since light is a form of energy, foot lasers harness this energy and dial it down to a range that energizes cells to encourage cell regeneration and tissue healing.
The most popular type of laser foot treatment uses dual lasers to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and stimulate circulation in the blood and lymphatic systems.
Which conditions respond best to foot laser therapy?
Foot lasers are especially effective in reducing inflammation, swelling, and pain. As such, the foot conditions that respond best to foot laser therapy are those with these characteristics.
They include:
- Neuroma – Thickening of the tissue surrounding nerves.
- Plantar fasciitis – Inflammation of the plantar tissue extending from the heel to the base of the toes.
- Diabetic ulcers – Ulcerations caused by changes in blood circulation in diabetic patients.
- Arthritis – A condition associated with joint degeneration.
- Tendonitis – Tendon-related pain caused by overuse, injury, or wear and tear.
Does laser foot therapy really work?
Clinical trials have shown a significant improvement in pain relief in patients with various foot conditions, including plantar fasciitis and chronic foot pain.
What to expect during your laser foot therapy session
For most people, foot laser therapy is painless, has no side effects, and does not require any anesthesia or post-procedure care. Some patients report a slight warming sensation during the procedure but nothing more.
A typical laser foot therapy session lasts fifteen minutes and does not require any special preparation.
The podiatrist will apply the laser to the affected area, allowing the laser beams to penetrate deep into your tissue to stimulate healing. After the session, you can carry on with your day as usual.
How many sessions do you need?
For less severe conditions, you can get significant relief within one or two sessions. However, with an increase in severity, you might need more sessions. Typically, your foot doctor might recommend up to six sessions for acute pain, while chronic conditions might require 12 or more sessions, spread out in two to three sessions per week.
Foot/Ankle Pain Injury
|
|
|
|
If you
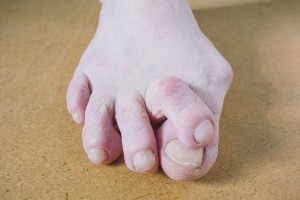
If you have toe deformities, chances are, your parents or their parents had them too. Many foot issues are inherited, and that includes digital deformities like bunions, hammertoes, mallet toes, claw toes, as well as overlapping and underlapping toes.
So, should you be worried about passing toe deformities on to your children?
While there’s a good chance that you might pass on your toe problems through your genes, the good news is that there are ways to treat them.
Do you have toe deformities, chances are, your parents or their parents had them too. Many foot issues are inherited, and that includes digital deformities like bunions, hammertoes, mallet toes, claw toes, as well as overlapping and underlapping toes. So, should you be worried about passing toe deformities on to your children? While there’s a good chance that you might pass on your toe problems through your genes, the good news is that there are ways to treat them.
- Bunion: A bunion is characterized by a bony growth from the side of the big toe joint, which, in turn, causes the big toe to point toward the other smaller toes. The bony spur can also develop on the outside of the pinky toe.
- Claw Toe: When you’ve got nerve damage in your toes, it can cause the joints in your toes to become weak. The joint at the base of the toe bends upward, while the rest of the toe slumps downward. It makes the toes look like it’s clawing the ground.
- Hammertoes: When the middle toe joint bends upward, making the toe’s shape look like an upside-down “V” that is called a hammertoe. It occurs because there is an imbalance in the muscles, tendons, or the ligaments of the feet.
- Mallet Toes: An additional deformity due to an imbalance of the muscles, tendons, or the ligaments of the feet is characterized by the toe joint closest to the toenail bending upward called mallet toes.
- Overlapping or underlapping toes: In some cases, the conditions exist from birth. The smaller toes are usually the ones affected. The muscles, tendons, ligaments, or bones are misaligned.
- In most cases, these toe deformities are treatable, especially when detected early. Some treatment options include:
- Toe Exercises: For some mild cases of toe deformity issues, strengthening the soft tissues around toes can help the toes regain their form.
- Taping: In the cases where the soft tissues just need a little help, taping the toes can help straighten them out.
- Splinting: If the toes are in bad form, they may be interfering with certain activities. Splinting them can help them become stronger while keeping them in good shape.
- Surgery : When non-invasive remedies don’t work, and the toe deformities are severe, it may be necessary to set the bones and/or loosen the tendons or ligaments that might be causing the toe deformity.
- So if you’ve got toe deformities, don’t fret! Come see our board-certified podiatrist Dr Mary Benjamin at Aveon Health. She can assess your feet, and find the best treatment for your toe problems.
Foot Deformity
In its normal form, the structure of the human foot allows us to walk in an upright position. Our feet consist of bones, joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments, which also keep everything in place. This makes them stable and strong, while at the same time being flexible and adaptable. Feet can become deformed as a result of external factors, like foot postures or certain diseases. Foot deformities may, but don’t always , cause problems, such as pain and walking difficulties. There are various types of foot deformities. Some are present at birth and some may develop over years of abuse.
Most people have slightly deformed feet. This is completely normal and usually doesn’t lead to any problems. Hardly anyone has “ideal” feet.
Bunions:
What are bunions?
A Bunion or Hallux Valgus is a progressive condition where your big toe starts to turn inward. When this happens, a bony protrusion forms on the inside of your toe. I time this process can force your big toe under or over your second toe, causing pain and discomfort or other issues as well.
Bunions aren’t dangerous but can cause a variety of problems Usually wearing shoes becomes difficult because shoes were not designed to accommodate the newly-forming bump. This alone will lead to increased pain and swelling. If this issue is not corrected, even wearing larger, more roomier shoes could still result is severe pain.
Another problem created by bunions are the formation of corns and calluses. This usually occurs when the bunion forces the big toe either over or under the second toe.
What causes bunions?
Considered to be affected by genetics, Bunions maybe genetic, which means that you may inherited this condition. However, shoes that crowd your toes does increase the development and progression of bunions and cause arthritis. That is why you should always wear a good quality, proper size shoe and for woman never wear shoe with heals higher than 2 inches.
How are bunions treated?
Bunionectomy:
Bunions are progressive which means without treatment, they will get worse. Wearing the proper footwear, adding orthotics and taking an anti-inflammatory medications may reduce the discomfort and may somewhat slow down the progression, it is inevitable that the bunions will get worse.
When your bunion has progressed to the point wearing shoes becomes painful or it interfers with your second toe ,surgery, may be recommended. This type of surgery is called a bunionectomy
Bunionectomy can be performed on an outpatient basis. When your surgery is complete you are free to return home on the same day. During the procedure, he shaves down the bone that’s forming the bump on the inside of your toe, rebalances the soft tissue in your foot, and repositions your metatarsal, keeping it in place with screws and plates.
Depending upon the extent of the surgery, some patients are able to walk afterward with the aid of a surgical shoe
Lapiplasty
Lapiplasty is a 3D Bunion Correction is an advanced surgical procedure that corrects a bunion by rotating the entire deviated bone back into its normal anatomical position. This is done using specially-designed instrumentation, naturally straightening your toe and removing the “bump” and associated pain. Innovative plating technology is used to permanently secure the unstable joint. Most patients are able to walk within days of surgery. No cast is required; allowing patients to get back to the shoe wear of their choice and activities quickly.
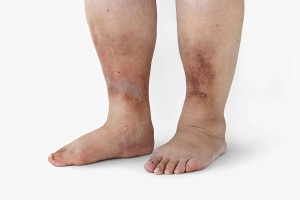
What Causes Lymphedema?
Lymphedema can be caused by cancer or by cancer treatment.
- Sometimes a cancerous tumor can get big enough to block the lymph system.
- Surgery to remove cancer may also remove lymph nodes or some of the vessels that carry the lymph fluid. This can cause the fluid to build up in surrounding tissues.
- Radiation treatment can damage the lymph vessels, resulting in too much lymph fluid in the tissues.
Can Lymphedema Be Prevented?
Before you have surgery or radiation treatment for cancer, ask your doctor what can be done to lower the chances that you will get lymphedema.
What Are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
The symptoms of lymphedema may include—
- Your arm, leg, or other part of your body has a little swelling at first, but gets bigger over time.
- The skin in that area feels tight, and sometimes has a tingling sensation.
- The arm or leg with lymphedema feels heavy.
- Clothing and jewelry fit more tightly on the affected area.
- The skin looks thicker or leathery.
If you notice any swelling after cancer treatment, talk to your doctor about what is causing it and how best to treat it.
What Health Problems Can Lymphedema Cause?
- Lymphedema raises your risk of getting an infection in the swollen area. This happens because the cells that prevent infection can’t reach that part of your body.
- Wounds may heal more slowly on the part of your body that has lymphedema.
- You may feel upset, depressed, embarrassed, or angry about the lymphedema.
- The joints in the part of the body with lymphedema may feel stiff or sore.
If I Have Lymphedema. What Should I Do?
It is very important to see a doctor right away to find out why you have swelling. You should make sure there is no other cause of the swelling that needs immediate treatment, like a blood clot.
How Is Lymphedema Diagnosed?
Dr Benjamin will examine you and ask you when you first noticed the problem. If your arm or leg is swollen, your doctor may measure it to compare it with your other arm or leg. Usually, if your swollen arm or leg is 2cm (about 4/5 of an inch) bigger than your other arm or leg, you have lymphedema.
Dr Benjamin may also suggest other tests to find out if you have lymphedema and if so, what is causing it. Lymphoscintigraphy is a test that uses radioactive material to see if the lymph vessels are blocked. Computed tomography(CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can take pictures of the swollen area to find out why the lymph vessels are blocked.
How Is Lymphedema Treated?
At this time, there is no cure for lymphedema. The goal of treatment is to reduce the swelling or keep it from getting worse, and to relieve symptoms. Your doctor can help you figure out which treatments are best for you.
Lymphedema can be treated with:
Exercise. Moving your swollen arm or leg may help the lymph fluid to drain, thus reducing the swelling.
A compression sleeve or stocking. This garment fits tightly on your swollen arm or leg, helping the lymph fluid flow out.
Massage therapy. A special kind of massage called manual lymph drainage can help push the lymph fluid out of the swollen part of your body.
A pneumatic pump. A machine inflates a sleeve that you place on your swollen arm or leg, helping lymph fluid flow out.
Weight loss. In patients who are overweight, lymphedema related to breast cancer may improve with weight loss.
Surgery. If your lymphedema is severe, your doctor may suggest that you get an operation. Dr Benjamin can provide information regarding the best surgeons in the area.
Cancer treatment. If a cancerous tumor is causing the lymphedema, the cancer is treated.
Tips for Living with Lymphedema:
The keys to managing lymphedema are preventing infections and allowing fluids to flow through the swollen area.
Prevent Infections:
- Keep your skin clean, and use lotion to keep it moist.
- If you get a small cut, clean it right away and apply antibacterial ointment and a bandage.
- Don’t get needle sticks (vaccines or blood tests) in the swollen area.
Allow Blood and Lymph Fluid to Flow Freely:
- Don’t wear tight clothing or jewelry.
- If you have lymphedema in one arm, have your blood pressure taken on, and blood drawn from, the other arm.
- If your arm or leg is swollen, elevate it above your heart when possible.
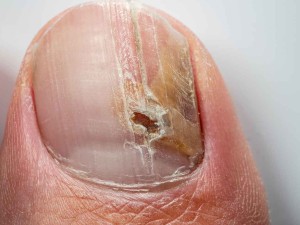
Fungus
Get a Diagnosis
Since toenail fungus can look like other conditions, including psoriasis, you’ll want to have your toenail checked by a doctor. You may need to see a specialist who cares for feet (a podiatrist) or skin (a dermatologist). They might scrape off some of the affected part and send it to a lab to figure out what’s causing the problem.
Treatment
The way you treat toenail fungus depends on which fungus you have and how bad the infection is. Your doctor may try one thing or a combination:
- A topical cream that goes directly on the nail
- A topical nail lacquer
- An antifungal prescription pill
- A laser treatment that removes the damaged area of the nail or skin
In some cases, you might need to have the nail removed completely with surgery.
Take care of your toes Use soap and water to wash your feet, and dry well, including between toes. Trim your toenails — straight across — to keep them shorter than the end of your toe. Make sure the tools you use are clean, too. Wash clippers and files with soap and water, then wipe with rubbing alcohol. You might be tempted to cover up discolored nails with polish, but don’t. Your nail bed can’t “breathe,” which keeps fungus from going away.
Keep Feet Dry and Clean
Be smart about your footwear. Choose socks that wick moisture away. Change them regularly or if they get damp or wet. Make sure your shoes fit well. They should be made of something that lets air move through it, like canvas, mesh, or leather. Wear shower shoes in wet public places like locker rooms and swimming pools.
Healthy Feet
You know your heart needs lots of TLC. Your feet do, too. After all, they are the workhorses of your body, taking about 5,000 steps a day. That’s 2.5 miles! Not to mention that your feet have to bear the weight of your body every step of the way. In addition, we cram them into shoes and stand on them for long periods of time. Those hard-working feet deserve a little more attention than you’re probably giving them. Here’s what you need to know.
Basic Care
What kind of basic care do my feet need?
Just as you wouldn’t go a day without brushing your teeth, you shouldn’t you go a day without taking care your feet.
- Check them daily for cuts, sores, swelling, and infected toenails.
- Give them a good cleaning in warm water, but avoid soaking them because that may dry them out.
- Moisturize them every day with lotion, cream, or petroleum jelly. Don’t put moisturizer between your toes. You want to keep the skin there dry to prevent infection.
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting shoes. Your shoes shouldn’t hurt your feet.
- Skip the flip-flops and flats. They don’t provide enough arch support.
- Rotate your shoes so you’re not wearing the same pair every day.
- Trim your toenails straight across with a nail clipper. Then use an emery board or nail file to smooth the corners, which will prevent the nail from growing into your skin.
How do I prevent corns and calluses?
- Wear shoes that fit your feet properly.
- Avoid wearing high heels every day.
- Use gel pad inserts to further cut down on rubbing and pressure on your foot.
How do I treat corns and calluses?
Mild corns and calluses don’t usually need treatment and will go away on their own. But there are some things you can do to help them go away more quickly:
- Wear thick socks to protect your skin.
- Rub your callus with a pumice stone while you’re in the bath or shower.
- Use corn pads to relieve pressure.
- Apply Salicylic to help dissolve corns and calluses. Be sure to follow directions carefully so you don’t damage healthy skin. Never use acid treatments on your feet if you have diabetes.
- Wear prescription foot orthotics.
Sweaty Feet
Why do my feet sweat so much?
Nobody knows exactly what causes some people to have really sweaty feet, also called Hyperhydrosis. It’s likely inherited. Most people sweat when it’s hot out, but people with Hyperhydrosis sweat all the time. Hyperhydrosis is more common in men than women and in younger adults.
What problems can sweaty feet cause?
Stress, medications, and hormonal changes can also trigger your body to sweat more.
Besides the discomfort of having wet feet, which could make you slip in your shoes, you could find that you have smelly feet and are prone to infections since that wetness can break down your skin.
How can I get my sweaty feet under control?
Start with good foot hygiene:
- Wash your feet with antibacterial soap. Make sure to clean between your toes.
- Dry your feet, and sprinkle them with cornstarch, foot powder, or Anti fungal powder.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks.
- Change socks frequently throughout the day.
Still can’t control it? See a doctor. Treatment options include prescription roll-on antiperspirants, Botox injections, iontophoresis (a treatment that temporarily plugs sweat glands) and surgery. There is a topical called Qbrexa (Glyprronium) that can be used to block the ability to sweat locally.
Foot Odor
What causes foot odor?
The two main culprits are sweating of the feet and your shoes. When your sweat mingles with the bacteria in your shoes and socks, it creates an odor.
How can I control foot odor?
Follow these tips:
- Wash your feet daily in warm water with mild soap. Dry them thoroughly.
- Dust your feet with baby powder or nonmedicated foot powder. You might also try applying an antibacterial ointment.
- Change your socks and shoes at least once a day.
- Wear shoes that let your feet breathe: leather, canvas, and mesh are good options, not nylon or plastic.
- Avoid wearing the same shoes 2 days in a row. For athletic shoes, rotate pairs so each has time to dry, allowing at least 24 hours to air out.
- Soak your feet in strong black tea (two tea bags per pint of water, boiled for 15 minutes and mixed with 2 quarts of cool water) 30 minutes a day for a week. Or use a solution of one part vinegar and two parts water.
Warts
What are warts?
These small growths of hardened skin are caused by a virus. They can be painful, especially when they develop on the bottom of your feet. Those are called plantar warts.
The most common way to catch them is by walking on a dirty, wet surface without shoes. If the virus touches your skin, it can enter through a cut, some so small you don’t even know you have them. The result could be a plantar wart, which may be hard, flat, and gray or brown in color.
How do I treat warts?
Don’t try to treat warts yourself. Your doctor may remove the wart with a laser or by minor surgery, or use liquid nitrogen or a prescription topical.
Although there are many over-the-counter wart treatments, you should only use them if your doctor advises it. You could accidentally mistake a wart for something like a skin cancer and delay getting the right treatment, and some of those gels and liquids contain acids or chemicals that may destroy otherwise healthy tissue. If you have diabetes, heart disease, or circulatory disorders, you should never use these treatments.
How can I prevent warts?
- Wear flip-flops in public showers, locker rooms, and pool areas.
- Change your shoes and socks every day.
- Keep your feet dry (warts thrive in moisture).
- Don’t touch other people’s warts or warts on other parts of your body.
Athlete’s Foot
What is athlete’s foot?
You don’t have to be an athlete to catch this condition. It’s caused by a fungus that thrives in warm, dark, humid environments (think dressing rooms, showers, and swimming pool locker rooms). Your bare feet come in contact with the fungus, which then takes up residence on your foot. Symptoms include dry skin, itchi9ng and burning, scaling, inflammation , blisters, and skin cracking.
The worst part? It spreads easily, especially to the soles of your feet and toenails. You can also spread the infection to other areas of your body just by scratching it and then touching yourself. You can even pick up athlete’s foot from bed sheets or clothes that have come in contact with the fungus.
How do I treat athlete’s foot?
Athlete’s foot can be hard to treat. See your doctor to make sure it is a fungus and not another condition.
Soaking your feet in warm water with Epsom Salt may provide some relief.
Your doctor may suggest an over-the-counter antifungal powder, cream, or spray or prescribe some medication you apply directly to your skin. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antifungal pills. Be sure to keep using your medication as directed, even if your symptoms have gone away. This will help prevent it from returning.
How can I prevent athlete’s foot?
- Wash your feet daily with soap and water.
- Take extra care to dry between the toes.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places.
- Keep your feet dry. If your feet sweat, use talcum powder and wear breathable shoes, like ones made from leather.
- Wear socks that wick moisture, and if you’re a heavy foot sweater, change socks often.
Insoles and Inserts
What are shoe inserts?
Shoe inserts can help with foot pain like flat arches and foot and leg pain. They provide extra support for different parts of your feet, like your heel, arch, or ball of the foot. You can get them over-the-counter.
They’re different from custom orthotics, which are prescribed by a doctor and designed for your feet.
A word of caution:
If you have diabetes or poor circulation, over-the-counter inserts may not work for you. Check with your doctor about your specific needs.
How do I find the best insert for my feet?
Choosing the right insert can be confusing, given how many are on store shelves. You need to know what you want the insert to do. Do you need additional arch support because you stand a lot at work? Are you a walker who wants a little extra padding in your sneakers? Here’s a quick guide that can help point you in the right direction.
- For low arches or flat feet: Arch support
- For extra cushioning: Insoles
- For extra cushioning in the heel: Heel liners or heel cups
- To prevent shoes rubbing against heels or toes: Foot cushions
If the store allows, spend a few minutes walking around with the insert in your shoe before you buy it. If you feel any discomfort, consider another insert.
Diabetes and Foot Health
How does diabetes affect foot health?
When you have diabetes, you are prone to getting the following foot complications:
- Foot ulcers and infections: Peripheral artery disease, a condition that reduces blood flow to the feet, is common in people with diabetes. It makes them more likely to get ulcers and infections. If you think you have an ulcer, which usually develops on the ball of the foot or bottom of the big toe, call your doctor immediately.
- Calluses: These thick areas build up faster and more often in people with diabetes. Talk with your doctor about treatment. One option may be therapeutic shoes.
- Neuropathy: Diabetes can cause nerve damage in your feet. As a result, you may not be able to feel pain, heat, or cold as well, which means a foot injury could go unnoticed. Nerve damage could even change the shape of your feet and toes, making it harder to wear regular shoes.
- Skin changes: Nerves control sweat and oil glands in your feet, but when they no longer work, your feet can get so dry that they peel and crack. Make sure you moisturize your feet every day. Avoid getting lotion between your toes.
Are there special things I can do for my feet if I have diabetes ?
- Follow proper foot hygiene.
- Check and wash your feet daily
Then add these extras to your to-do list:
- Move more. Exercise improves circulation in the legs and feet, so consider starting a walking program. Walking can be done anywhere, like inside at a mall. All you need are good shoes.
- Avoid going barefoot. Wear shoes and socks that fit well and offer protection.
- Protect feet from temperature changes. Because of nerve damage, you may not feel heat and cold as well, so make sure you don’t burn or freeze your feet. Avoid putting them in hot water. Skip hot water bottles, heating pads, and electric blankets. Wear shoes on the beach or hot pavement.
- Keep the blood pumping. Help keep blood flowing in your feet by propping them up when sitting. Move your ankles around and wiggle your toes for 5 minutes two to three times a day. Also, try not to sit with crossed legs for long periods of time.
- Moisturize daily. Treat the tops and bottoms of your feet — but not between your toes — with a moisturizing lotion.
- Stop smoking. Smoking can cause arteries to harden faster, which contributes to poor circulation.
What are the main causes of foot pain?
Each of your feet contains 26 bones and, together, account for one-quarter of the bones in your body. Helping your bones support your body and provide mobility are soft tissues, including your muscles, tendons, and ligaments. In other words, for such small areas, your feet are incredibly complex structures, which means that there’s a lot that can go wrong, causing you pain.
The leading causes of foot pain are:
-
Arthritis
-
Trauma or injury
-
Bursitis
-
Fractures
-
Sprains
-
Tendinitis
-
Peripheral neuropathy
-
Stone bruises
-
Structural issues, such as flatfoot or high arches
-
Bunions
-
Hammertoes
This long list only covers the most common causes of foot pain, but the fact is that given all that your feet endure, day in and day out, foot pain is not at all uncommon and can be caused by any number of conditions.
What causes heel pain?
Far and away the leading cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot from your heel to the base of your toes. Outside of plantar fasciitis, heel pain can also be caused by:
-
Heel spurs
-
Stone bruises
-
Bursitis
-
Achilles tendon problems
-
Fractures
-
Arthritis
If you consider that for every mile you walk, you place 60 tons of stress on each heel, it’s little wonder that heel pain can, and does, crop up from time to time.
How are foot and heel pain treated?
First a comprehensive exam is conducted to evaluate and determining the cause and range of pain. Upon Review of your symptoms and using diagnostic imaging to get a better look at the internal structure, your doctor can diagnose the issue.
Once he identifies the source of your foot or heel pain, your Doctor will come up with an appropriate treatment plan that may include one or more of the following:
-
Medications for inflammation and pain
-
Custom orthotics
-
Physical therapy
-
Splinting, bracing, or a cast
-
Rest
-
Corticosteroid injections


